Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that includes virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). These immersive technologies are revolutionizing many industries, and healthcare is no exception. By creating realistic simulations and enhancing real-world environments, XR holds the potential to significantly improve both training for healthcare professionals and the care provided to patients. This article explores how XR is transforming healthcare by enhancing medical training, patient care, and therapeutic interventions. We will also discuss the current challenges and the future possibilities of XR in the healthcare industry.
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality (VR) is a fully immersive experience where users are placed in a digitally generated environment. In healthcare, VR can be used to simulate surgeries, diagnose conditions, and create an interactive environment for medical students to practice their skills.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital elements on the real world. In healthcare, AR can assist doctors by providing real-time data, such as patient information or anatomical visuals, overlaid on a patient’s body or in a surgical setting.
Mixed Reality (MR)
Mixed Reality (MR) combines both AR and VR. It allows physical and digital objects to coexist and interact in real-time. MR is used in healthcare to visualize medical data alongside real-world objects, enhancing the precision of surgeries and medical procedures.

The Role of XR in Medical Training
Surgical Training
Surgical training has traditionally relied on cadaver dissections and live surgeries. However, XR technologies provide innovative solutions to improve the quality and accessibility of surgical education. VR simulations, for example, allow medical students and surgeons to practice complex procedures in a risk-free virtual environment. These simulations can mimic real-world scenarios with high levels of accuracy, allowing trainees to practice repeatedly and learn from their mistakes without the fear of harming patients.
With MR, surgeons can practice surgeries using holographic representations of the patient’s anatomy. This level of precision and customization enhances the understanding of individual patient needs, leading to better outcomes.
Anatomy and Physiology Education
Anatomy and physiology are core components of medical training. Traditionally, students have relied on 2D images or cadavers to understand the human body. However, XR technologies are transforming how these subjects are taught. AR and VR can create 3D models of human anatomy, allowing students to explore and manipulate organs, muscles, bones, and systems in a fully immersive environment.
This interactive approach helps students understand complex structures and processes better. For example, VR can allow students to explore the human heart in 3D, providing them with a more tangible understanding of how blood flows and how various conditions affect the heart.
Remote Training and Collaboration
Another significant benefit of XR in medical education is the ability to offer remote training. With XR technologies, healthcare professionals from anywhere in the world can attend virtual classes, participate in remote surgeries, or collaborate with peers in real-time. VR and MR enable healthcare professionals to interact with mentors and colleagues virtually, overcoming geographical limitations.
In the context of surgery, remote training platforms allow surgeons to observe procedures in real-time from anywhere. They can even practice procedures using VR simulators, improving their skills before performing real surgeries.
Enhancing Patient Care through XR
Pain Management
XR technologies have been shown to be highly effective in reducing pain perception for patients. VR, in particular, has gained popularity as a tool for pain management. Studies have demonstrated that immersive VR environments can distract patients from painful stimuli during medical procedures. For example, VR has been used to manage pain during burn wound care, dental procedures, and chemotherapy.
By immersing patients in a calming and engaging virtual environment, VR helps redirect their attention, reducing their anxiety and perception of pain. This has been especially beneficial for pediatric patients and those with chronic pain conditions.
Psychological Therapy and Mental Health
Beyond pain management, XR technologies have proven effective in treating various mental health conditions. VR, AR, and MR are used for exposure therapy in patients with phobias, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and anxiety. VR simulations can recreate scenarios that trigger anxiety or fear in a controlled and gradual manner, helping patients confront their fears in a safe environment.
Additionally, VR has been used in cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for depression and anxiety, providing patients with virtual environments where they can practice coping strategies, relaxation techniques, or problem-solving in challenging situations.
Physical Rehabilitation
XR technologies are also making a significant impact on physical rehabilitation. VR can be used to create engaging, interactive environments that motivate patients to perform therapeutic exercises. For patients recovering from strokes, accidents, or surgeries, these exercises are often repetitive and monotonous, which can hinder their progress.
By incorporating gamification into rehabilitation, XR technologies help maintain patient interest and improve adherence to therapy. For example, VR systems can track the patient’s movements, provide real-time feedback, and even gamify the rehabilitation process, creating a more enjoyable and rewarding experience.
Additionally, MR can be used in physical therapy to overlay digital information, such as the patient’s movements or corrective guidance, onto the real world. This allows therapists to provide real-time instructions and guidance during physical rehabilitation sessions.

Surgical Planning and Visualization
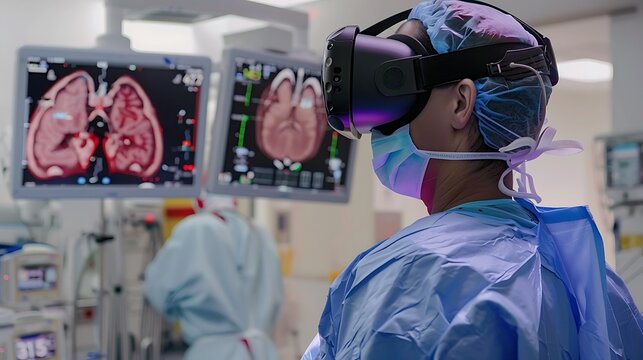
Surgical planning and visualization are critical aspects of ensuring the success of complex medical procedures. XR technologies have become invaluable tools for improving pre-surgical planning. Surgeons can use VR or MR to visualize and interact with 3D models of patients’ anatomy, based on their medical scans (CT scans, MRIs, etc.). This enables surgeons to plan more accurately and customize procedures to the unique characteristics of each patient.
Intraoperative MR and AR technologies can assist surgeons during the procedure by overlaying digital information onto the patient’s body. This can include live imaging, real-time vital statistics, or anatomical landmarks that guide the surgeon in making precise incisions and avoiding critical structures.
XR in Patient Education
Patient education is a key component of effective healthcare. XR technologies allow healthcare providers to present complex medical information in an engaging and interactive way. Instead of relying on brochures or verbal explanations, healthcare professionals can use AR or VR to show patients their diagnosis, treatment options, and potential outcomes in a visually compelling manner.
For example, VR can be used to explain how a patient’s condition affects their body, such as a heart disease or a joint disorder, by simulating the internal processes. This helps patients gain a better understanding of their health and treatment plan, leading to better-informed decision-making and improved health outcomes.
Challenges in Implementing XR in Healthcare
High Costs
One of the major challenges in the widespread adoption of XR in healthcare is the high initial cost of the technology. VR and MR systems can be expensive to purchase and maintain, and the development of high-quality content (e.g., realistic simulations or 3D models) requires substantial investment. This financial barrier limits access to XR technologies, particularly in resource-limited healthcare settings.
Generative AI: The Virtual Assistant Transforming Healthcare
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
As with any technology that handles sensitive personal data, data security and privacy are crucial considerations in the implementation of XR in healthcare. XR systems may collect data on patient movements, medical conditions, and interactions with virtual environments. Ensuring that this data is securely stored and protected from unauthorized access is critical to maintaining patient confidentiality and trust.
Technical Limitations
While XR technologies have advanced significantly, there are still technical limitations that hinder their widespread use in healthcare. For example, VR simulations may not yet fully replicate the tactile feedback required for certain medical procedures, such as surgeries. Additionally, some MR systems may suffer from issues with latency, which can affect the quality of real-time guidance during surgeries.
The Future of XR in Healthcare
Increased Accessibility
As the technology behind XR continues to evolve, the costs associated with it are likely to decrease. This would allow more healthcare institutions, particularly those in underserved areas, to implement XR systems in training and patient care. Moreover, advancements in mobile XR devices (such as smartphones and standalone VR headsets) will make it easier for healthcare professionals and patients to access XR tools on a wider scale.
Personalized Medicine
With the integration of XR and artificial intelligence (AI), the future of healthcare will likely involve even more personalized treatment options. XR can be used in conjunction with AI to create tailored simulations and interventions based on a patient’s unique medical data. For instance, a patient’s virtual model could be used to simulate and test various treatment strategies before choosing the best course of action.
Integration with Other Technologies
The future of XR in healthcare also lies in its integration with other emerging technologies such as robotics, 3D printing, and IoT. For example, XR could be used alongside robotic surgery to offer real-time guidance and assistance during procedures. Additionally, 3D printing could be used to create personalized medical devices or implants, which can then be visualized in XR environments.
Extended Reality (XR) is ushering in a new era of healthcare innovation. From revolutionizing medical training to enhancing patient care and rehabilitation, XR technologies have the potential to reshape the healthcare landscape. While there are challenges to overcome, including cost and data security concerns, the benefits of XR in healthcare are undeniable. As these technologies continue to evolve and become more accessible, XR will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in improving healthcare delivery worldwide.

