Osteoporosis is a serious bone condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly women. This disease causes bones to become weak and brittle, leading to an increased risk of fractures. While osteoporosis often develops without noticeable symptoms, it is a condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. In this article, we will explore the various ways women can prevent osteoporosis, including lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, physical activity, and regular medical checkups.
What is Osteoporosis?
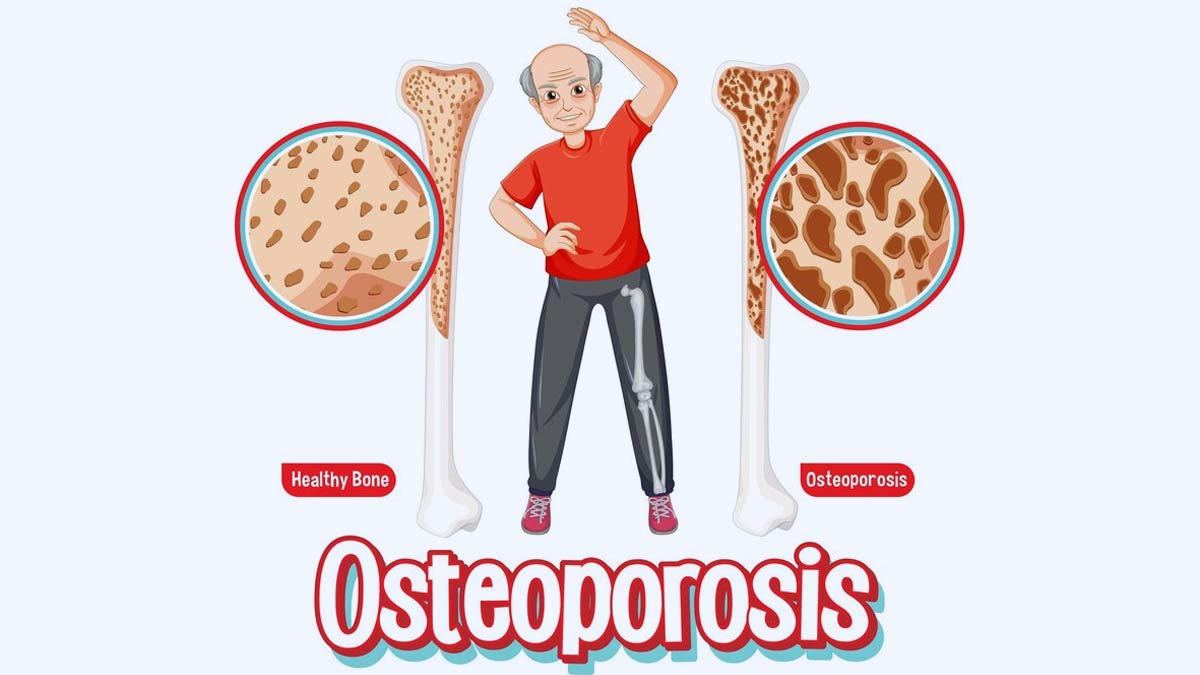
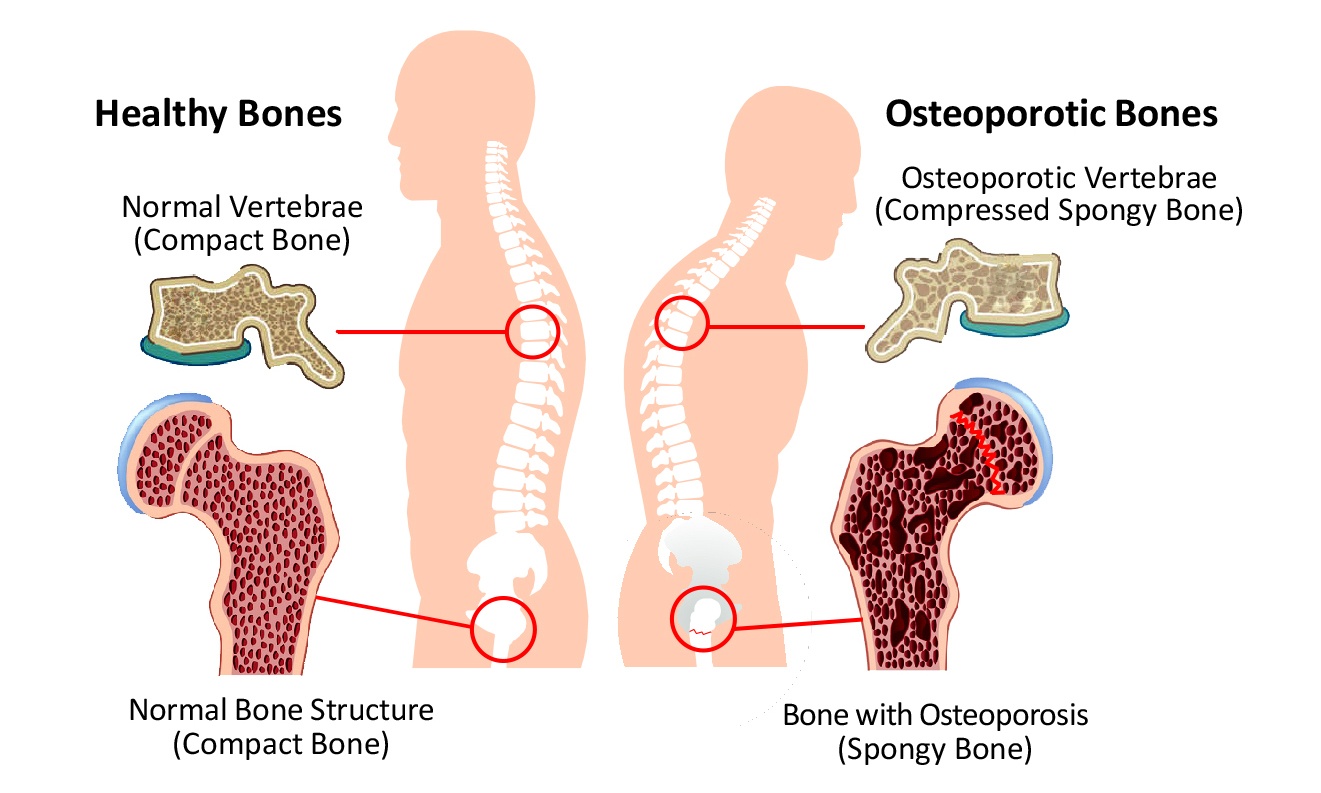
Osteoporosis is a condition in which bones lose density and strength, making them more susceptible to fractures. It occurs when the body either loses too much bone mass or does not make enough bone mass. The result is a fragile skeleton that can break easily, often from minor falls or even from actions like bending over or lifting objects.

While osteoporosis can affect both men and women, women are at a higher risk, particularly after menopause. This is because the decrease in estrogen production during menopause accelerates bone loss. Without adequate bone mass, bones become porous, brittle, and weak.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis in Women
Understanding the risk factors for osteoporosis is essential for prevention. Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis due to the following factors:
- Age: As women age, bone density naturally decreases, especially after menopause.
- Menopause: A significant drop in estrogen levels after menopause accelerates bone loss.
- Family History: A family history of osteoporosis can increase the risk, indicating a genetic component to the disease.
- Body Size: Women with small body frames are at greater risk because they have less bone mass to lose over time.
- Dietary Factors: Poor nutrition, especially low calcium and vitamin D intake, increases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to bone loss.
- Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and heavy drinking both contribute to bone weakening.
By understanding these risk factors, women can take proactive steps to reduce their chances of developing osteoporosis.
How to Prevent Osteoporosis in Women
While genetics and age may be factors beyond your control, there are several proactive steps that women can take to maintain bone health and prevent osteoporosis. These include dietary changes, exercise, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical checkups.
The Role of Family Activities in Wellness: Enhancing Health and Well-Being Together
1. Consume a Bone-Healthy Diet
A nutritious diet is one of the most important factors in preventing osteoporosis. The bones need specific nutrients to remain strong and healthy. The two most critical nutrients for bone health are calcium and vitamin D.
Calcium
Calcium is the primary mineral found in bones, and adequate intake is essential for maintaining bone density. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends that women under 50 consume 1,000 mg of calcium daily, and women over 50 should increase their intake to 1,200 mg daily. Good sources of calcium include:
- Dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens)
- Fortified cereals and plant-based milks (almond, soy, or oat milk)
- Fish with edible bones (salmon, sardines)
If you have difficulty getting enough calcium from food, calcium supplements may be an option. However, it’s important not to exceed the recommended daily intake, as excessive calcium can lead to kidney stones or interfere with other nutrient absorption.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption in the body. Without sufficient vitamin D, your body cannot effectively absorb calcium, regardless of how much you consume. The recommended daily intake of vitamin D for women is 600 IU for those under 70 and 800 IU for those over 70. Good sources of vitamin D include:
- Sun exposure (about 10-30 minutes of sunlight a few times a week, depending on skin type)
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Fortified foods (cereals, milk, orange juice)
- Egg yolks
For women at risk of deficiency, vitamin D supplements can help ensure adequate levels.
2. Engage in Weight-Bearing Exercise
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to strengthen bones and prevent osteoporosis. Weight-bearing exercises, in particular, stimulate bone formation and increase bone density. These exercises include activities that make you work against gravity, such as:
- Walking or hiking
- Jogging or running
- Dancing
- Stair climbing
- Strength training with weights
Strength training, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, is particularly effective in increasing bone strength because it helps maintain or build muscle mass, which in turn supports bone health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of weight-bearing exercise on most days of the week.
In addition to weight-bearing exercises, balance exercises such as tai chi or yoga can improve coordination and prevent falls, which is crucial for individuals with weakened bones.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for osteoporosis. Nicotine and other chemicals in tobacco smoke interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium, making bones more likely to become brittle. Women who smoke are also at greater risk of early menopause, which can accelerate bone loss.
Quitting smoking can significantly improve bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. If you smoke, consider seeking support from a healthcare professional or smoking cessation programs to help you quit.
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption is another risk factor for osteoporosis. Drinking too much alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb calcium and affect bone metabolism. Additionally, heavy drinking can increase the risk of falls, which can result in fractures in individuals with weakened bones.
Women should limit alcohol consumption to no more than one drink per day to help protect their bones. If you find it difficult to control your alcohol intake, seeking help from a healthcare provider or support groups can be beneficial.
5. Ensure Proper Hormonal Balance
For women, hormonal changes play a significant role in bone health. Estrogen, in particular, is essential for maintaining bone density. After menopause, when estrogen levels drop, women experience a faster rate of bone loss, making osteoporosis prevention even more critical.
In some cases, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be recommended to help maintain estrogen levels and reduce bone loss. However, HRT has risks and benefits, so it’s essential to discuss this option with a healthcare provider to determine if it’s right for you.
For women who cannot take HRT, other medications may help prevent bone loss, such as bisphosphonates, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), or denosumab. Your doctor can advise you on the best course of action based on your health history and risk factors.
6. Get Regular Bone Density Screenings
Bone density testing, also known as a DEXA scan, is a vital tool for diagnosing osteoporosis. Women over 65 should have a bone density test, and those under 65 may need one earlier if they have risk factors for osteoporosis. Early detection can help you take steps to prevent fractures and other complications associated with osteoporosis.
A bone density test measures how much bone mineral content you have in specific areas, such as the spine, hips, and wrists. If the test reveals that you have low bone density, your healthcare provider will recommend a treatment plan to help prevent further bone loss.
7. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being underweight increases the risk of osteoporosis. Women with low body weight have less bone mass and may experience bone loss more rapidly. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential for overall bone health.
However, it’s important to avoid excessive weight gain, as obesity can also lead to other health problems. Strive to maintain a healthy weight by combining a nutritious diet with regular physical activity.
8. Stay Informed and Consult a Healthcare Professional
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring your bone health. Your doctor can help assess your risk for osteoporosis and recommend preventive measures. For women with a family history of osteoporosis or other risk factors, early intervention is key to managing bone health.
Ask your healthcare provider about calcium and vitamin D supplementation, medications, and lifestyle changes that can help protect your bones.
Osteoporosis is a preventable condition, and women can take many steps to safeguard their bone health. By following a bone-healthy diet, engaging in weight-bearing exercise, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and seeking medical guidance, women can reduce their risk of osteoporosis and maintain strong, healthy bones throughout their lives.
The Importance of Family Health History in Preventative Care
Taking proactive steps now to protect your bones can lead to a better quality of life as you age, reducing the risk of fractures and promoting overall health. With the right care and lifestyle choices, osteoporosis can be managed or even prevented, allowing women to live life fully and confidently.