In today’s digital age, protecting sensitive information is a top priority for individuals and businesses alike. As data breaches and cyberattacks become increasingly prevalent, the need for robust security measures has never been more critical. One such measure is data encryption, a process that transforms information into a secure format that unauthorized parties cannot read. This article delves into the concept of data encryption, how it works, and why it’s essential for safeguarding information in the modern world.
Understanding Data Encryption
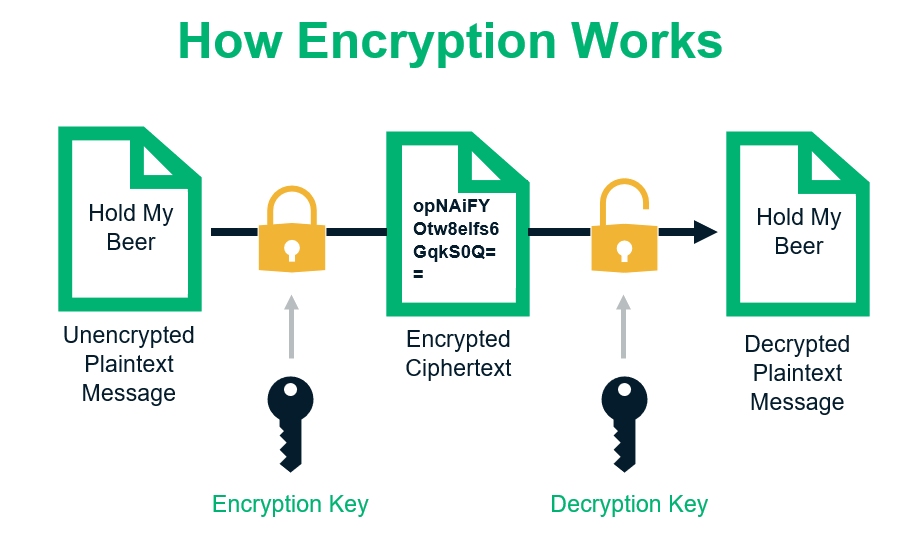
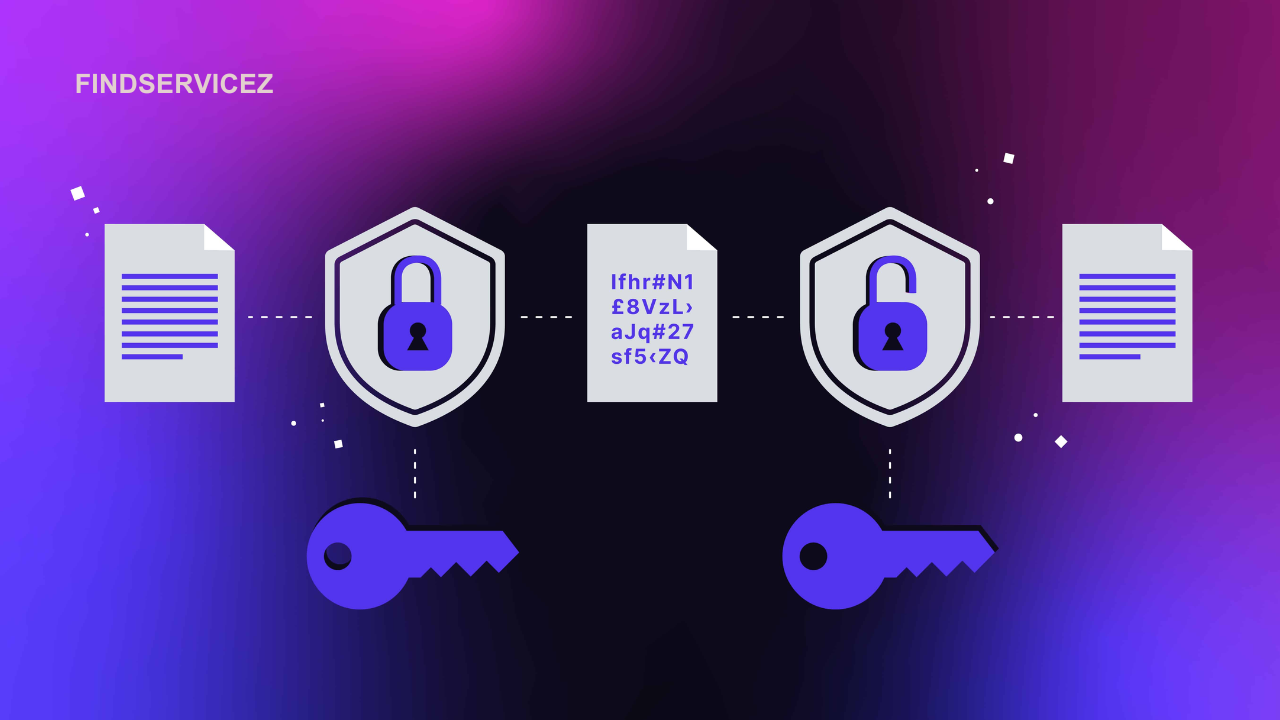
Data encryption is a security technique that converts readable data, known as plaintext, into an unreadable format called ciphertext. This transformation ensures that only authorized parties with the appropriate decryption key can access the original information. Encryption plays a crucial role in securing sensitive data, such as financial transactions, personal information, and confidential business communications.
The process of encryption is rooted in cryptography, the science of encoding and decoding information. Cryptography has evolved significantly over the centuries, from ancient techniques like Caesar cyphers to advanced algorithms used in modern encryption systems. Today, encryption is a cornerstone of cybersecurity, enabling secure communication and data protection across various platforms.
How Data Encryption Works
The encryption process involves two key components: the encryption algorithm and the encryption key. The algorithm is a mathematical formula that dictates how data is transformed, while the key is a unique string of characters used to encode and decode the information. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how data encryption works:
- Plaintext Input: The process begins with the original data, known as plaintext, which can include text, images, or other digital information.
- Encryption Algorithm: The plaintext is processed through an encryption algorithm, which applies complex mathematical operations to scramble the data.
- Encryption Key: A key is used in conjunction with the algorithm to generate the ciphertext. The key is a critical element that determines how the data is encrypted and decrypted.
- Ciphertext Output: The output of the encryption process is ciphertext, an unreadable format that cannot be interpreted without the corresponding decryption key.
- Decryption: To access the original information, the ciphertext must be decrypted using the appropriate key and decryption algorithm.
Types of Encryption
Data encryption comes in various forms, each designed to address specific security needs. The two main types of encryption are symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. This method is efficient and fast, making it suitable for encrypting large amounts of data. However, the challenge lies in securely sharing the key between parties. If the key is compromised, the encrypted data becomes vulnerable.
Common symmetric encryption algorithms include:
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): Widely used in modern encryption, AES offers robust security with key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits.
- Data Encryption Standard (DES): An older encryption method that has been largely replaced by AES due to its shorter key length and weaker security.
- Triple DES (3DES): An enhancement of DES that applies the encryption process three times for added security.
Asymmetric Encryption

Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key encryption, uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method eliminates the need to share a single key and is commonly used for secure communication and digital signatures.
Popular asymmetric encryption algorithms include:
- RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman): A widely used algorithm for secure data transmission and digital signatures.
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC): Known for its strong security with shorter key lengths, ECC is used in applications like SSL/TLS certificates and mobile devices.
Applications of Data Encryption
Data encryption is a versatile technology with applications across various domains. Some of the most common uses include:
Secure Communication
Encryption is essential for ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of digital communications. Technologies like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) use encryption to protect data transmitted over the internet, such as emails, instant messages, and web browsing sessions.
Data Storage
Organizations use encryption to safeguard sensitive data stored on servers, databases, and devices. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the storage medium, the data remains protected.
Financial Transactions
Addressing Student Burnout in Digital Classrooms: A Growing Concern
Encryption plays a critical role in securing online payments and financial transactions. Payment processors, banks, and e-commerce platforms use encryption to protect sensitive information like credit card numbers and account details.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, encryption is used to protect patient records and comply with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This ensures that sensitive medical information remains confidential.
Government and Defense
Governments and defence organizations rely on encryption to protect classified information and secure communications. Encryption technologies are also used to safeguard critical infrastructure and prevent cyberattacks.
Benefits of Data Encryption
Encryption offers several advantages that make it an indispensable tool for data protection:
- Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that sensitive information remains private and can only be accessed by authorized parties.
- Data Integrity: By protecting data from unauthorized modifications, encryption helps maintain its accuracy and reliability.
- Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that mandate the use of encryption to protect sensitive data, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Enhanced Security: Encryption provides an additional layer of security, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that sensitive information is encrypted gives individuals and organizations confidence in their data security measures.
Challenges and Limitations of Data Encryption

While encryption is a powerful tool, it is not without its challenges. Some of the common limitations include:
- Key Management: Ensuring the secure storage and distribution of encryption keys is a complex and critical task. Poor key management can compromise the entire encryption system.
- Performance Impact: Encryption processes can consume significant computational resources, potentially affecting system performance.
- Human Error: Mistakes in implementing encryption protocols or handling keys can lead to vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with encryption standards and regulations can be challenging, especially for organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions.
- Sophisticated Attacks: Advanced cyber threats, such as brute-force attacks and quantum computing, pose potential risks to encryption systems.
The Future of Data Encryption
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the field of encryption. Emerging trends and innovations are shaping the future of data security:
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: With the advent of quantum computing, traditional encryption methods may become vulnerable. Researchers are developing quantum-resistant algorithms to address this challenge.
- Homomorphic Encryption: This advanced encryption method allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it, enabling secure data analysis.
- Blockchain and Encryption: Cryptographic techniques are integral to blockchain technology, providing secure and transparent transaction records.
- Zero-Trust Security Models: Encryption plays a key role in zero-trust architectures, which require continuous verification of user and device identities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to enhance encryption techniques, improve key management, and detect potential vulnerabilities.
Preparing Parents for Hybrid Learning Models: A Comprehensive Guide
Data encryption is a vital component of modern cybersecurity, offering robust protection for sensitive information in an increasingly interconnected world. By understanding how encryption works and its various applications, individuals and organizations can take proactive steps to safeguard their data. Despite its challenges, encryption remains a cornerstone of digital security, paving the way for a safer and more secure future. Whether protecting personal information, securing financial transactions, or complying with regulatory requirements, encryption is an essential tool in the fight against cyber threats.