In recent years, research has increasingly focused on the critical role that gut health plays in maintaining overall wellness. While many of us are aware of the importance of nutrition, exercise, and sleep, gut health is an often-overlooked factor that influences much more than just digestion. Emerging science reveals that a healthy gut is essential for numerous bodily functions, from immune system support to mental health, skin condition, and even weight management.
This article will explore the profound connection between gut health and overall wellness, highlighting how the gut microbiome impacts various aspects of our health. We will also look at how to foster a healthy gut, the signs of gut imbalance, and the impact of diet and lifestyle choices on our microbiome.
What is Gut Health?
Gut health refers to the well-being of the gastrointestinal (GI) system, which includes not only the stomach and intestines but also the microbiome — the trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes, that live in our digestive tract. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining digestion, metabolism, and overall bodily functions.
The gut microbiome is a dynamic and diverse ecosystem that aids in the breakdown of food, production of essential nutrients, regulation of the immune system, and even communication with the brain. When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to a range of health problems, from digestive issues like bloating and constipation to more serious conditions like autoimmune diseases, obesity, and mental health disorders.
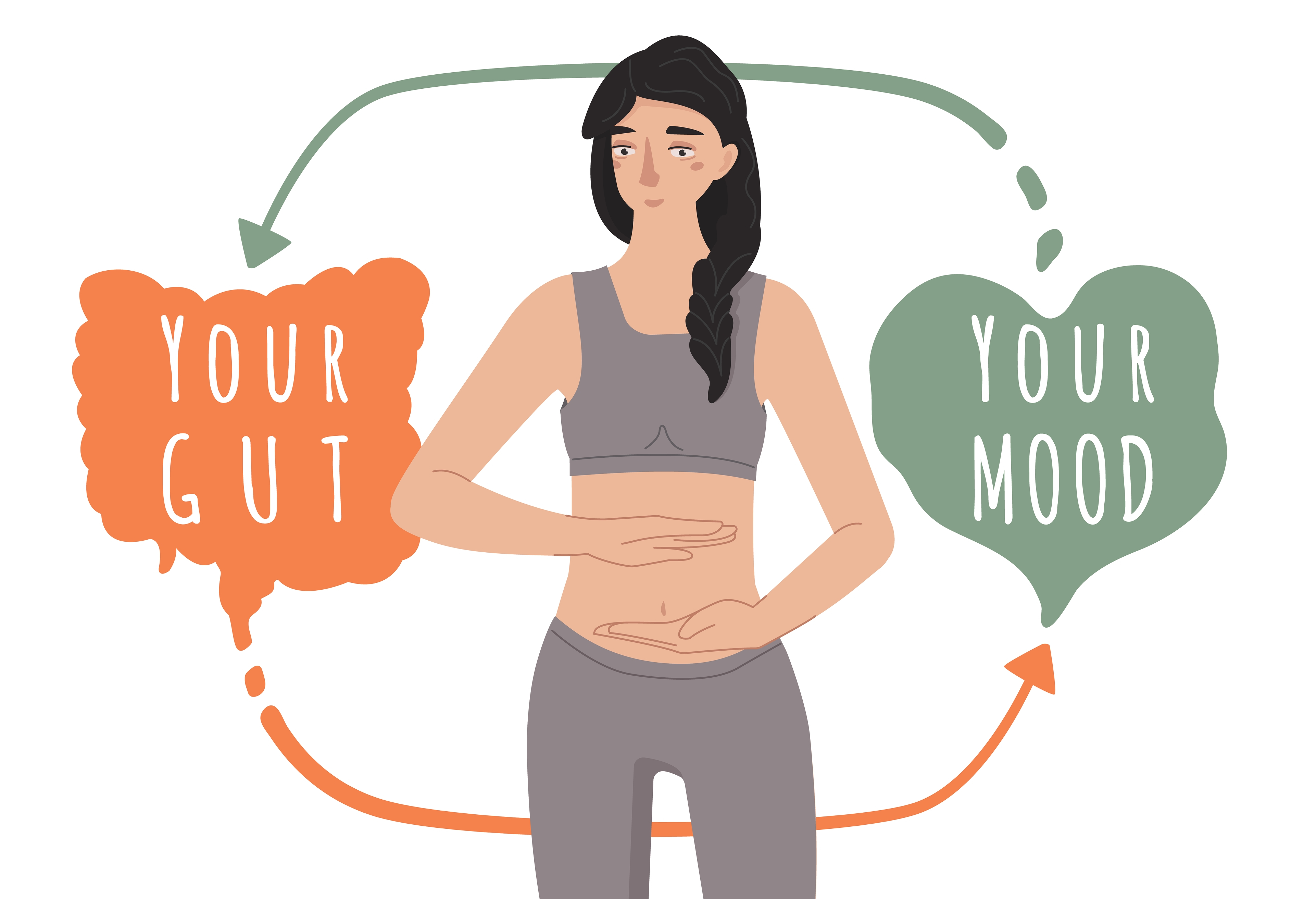
The Gut-Brain Axis: Gut Health and Mental Wellness
One of the most fascinating areas of research concerning gut health is its connection to mental health. The gut and brain are closely linked through a complex network known as the gut-brain axis. This two-way communication system allows signals to travel between the brain and the gut via the vagus nerve, which plays a critical role in regulating mood, stress responses, and emotional well-being.
Studies have shown that the gut microbiome can influence brain function and behavior. A healthy gut promotes the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which is responsible for regulating mood and emotions. In fact, it is estimated that around 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut. Conversely, an unhealthy gut microbiome may lead to imbalances in these chemicals, contributing to mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, and even conditions like autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
For example, researchers have found that individuals with depression often have an imbalance in their gut microbiome, which may contribute to their symptoms. On the other hand, interventions such as probiotics or dietary changes that improve gut health have shown promising results in improving mood and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Gut Health and Immune Function
The gut is a key player in the body’s immune system. About 70% of the immune system is located in the gut, specifically in the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). This large immune structure works in partnership with the gut microbiome to help defend against harmful pathogens and regulate immune responses.
A balanced gut microbiome plays a critical role in maintaining immune function. Beneficial bacteria in the gut support the production of antibodies, while also helping to regulate the activity of immune cells such as T cells. When the gut microbiome is imbalanced — a state known as dysbiosis — it can trigger chronic inflammation, weaken immune responses, and increase the risk of autoimmune diseases.
Chronic gut inflammation has been linked to a variety of health conditions, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease, and other autoimmune disorders. Therefore, nurturing a healthy gut is a key strategy in boosting immunity and preventing chronic illness.
Gut Health and Digestion
Perhaps the most obvious connection between gut health and overall wellness is the digestive system. A healthy gut is essential for the proper breakdown and absorption of nutrients, which are vital for the body’s energy production, cell repair, and overall growth. When the digestive system is functioning optimally, the body can efficiently absorb vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients that support various bodily systems.

An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to digestive problems such as bloating, gas, heartburn, and constipation. More severe conditions like IBS, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis can also stem from gut microbiome imbalances.
For instance, SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth) is a condition where an abnormal increase in the number of bacteria in the small intestine leads to bloating, abdominal pain, and malabsorption of nutrients. It is often associated with poor gut health and can significantly impair digestive function.
Gut Health and Skin Conditions
The link between gut health and skin wellness is another growing area of research. This connection, often referred to as the gut-skin axis, suggests that an imbalance in the gut microbiome can contribute to a variety of skin conditions, including acne, eczema, rosacea, and psoriasis.
One theory behind this is that an imbalanced gut microbiome can lead to increased inflammation in the body, which can, in turn, manifest as skin problems. Additionally, the gut plays a role in detoxification and the elimination of waste products through the liver. A compromised gut may lead to a buildup of toxins in the body, which can negatively affect the skin.
In contrast, promoting gut health through a balanced diet, probiotics, and prebiotics may improve skin conditions by reducing systemic inflammation and promoting a healthier immune response.
Gut Health and Weight Management
Recent research has also uncovered a strong link between gut health and body weight. The composition of the gut microbiome may play a significant role in regulating metabolism and fat storage. Certain strains of bacteria in the gut are associated with higher levels of fat absorption and may contribute to obesity, while others are linked to weight loss.
Gut bacteria influence the body’s ability to extract energy from food, store fat, and regulate hunger signals. Studies have shown that individuals with a diverse gut microbiome tend to have healthier body weight and better metabolism compared to those with a less diverse microbiome.
Additionally, the gut microbiome may impact insulin sensitivity, a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. An imbalance in gut bacteria may lead to insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of obesity and metabolic diseases.
Tips for Promoting a Healthy Gut
The good news is that gut health can be improved and maintained through conscious dietary and lifestyle choices. Here are some practical steps to enhance gut health:
1. Eat a Diverse Range of Foods
A diverse microbiome is linked to better gut health. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet will provide the necessary fiber and nutrients to support a healthy gut. Fiber acts as food for beneficial bacteria and promotes the growth of a diverse microbiome.
2. Incorporate Fermented Foods
Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso are rich in probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that can help maintain a healthy gut. Regular consumption of fermented foods can help replenish the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
3. Consume Prebiotic Foods
Prebiotics are compounds found in certain foods that feed and support the growth of beneficial bacteria. Foods such as garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus are rich in prebiotics and can promote the health of your microbiome.
4. Limit Processed Foods and Sugar
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and artificial sweeteners can negatively impact gut health by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria and reducing the diversity of beneficial microbes. Cutting back on these foods can help maintain a healthier gut microbiome.
5. Take Probiotic Supplements
For individuals with gut imbalances, taking probiotic supplements may help restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
6. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively affect gut health by altering the balance of gut bacteria and increasing gut permeability (also known as “leaky gut”). Practicing stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing, and exercise can help improve gut health.
7. Get Enough Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall wellness, including gut health. Poor sleep can disrupt the gut microbiome and lead to digestive issues and inflammation. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night to support a healthy gut.
Gut health is at the foundation of overall wellness, influencing everything from immune function and mental health to digestion and weight management. The gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in maintaining bodily systems, and disruptions to its balance can lead to a host of health problems. By nurturing a healthy gut through proper nutrition, stress management, and lifestyle choices, we can support not only our digestive health but our mental, emotional, and physical well-being.
Taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy gut can enhance quality of life, reduce the risk of chronic disease, and improve our ability to thrive. As research continues to uncover the intricate relationship between gut health and wellness, it’s clear that investing in the health of your gut is an investment in your overall health.


