Allergies are a significant concern for parents, particularly when it comes to their children’s health and well-being. The immune system of a child can be more sensitive to environmental, food, or seasonal triggers, leading to uncomfortable and sometimes dangerous allergic reactions. Understanding common allergies in kids, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing how to manage them effectively are vital steps for safeguarding your child’s health.
This comprehensive guide explores common allergies in kids, the signs to look for, and practical strategies to manage and treat these allergies. We also cover prevention tips to reduce the risk of allergic reactions and provide advice on when to seek medical help.
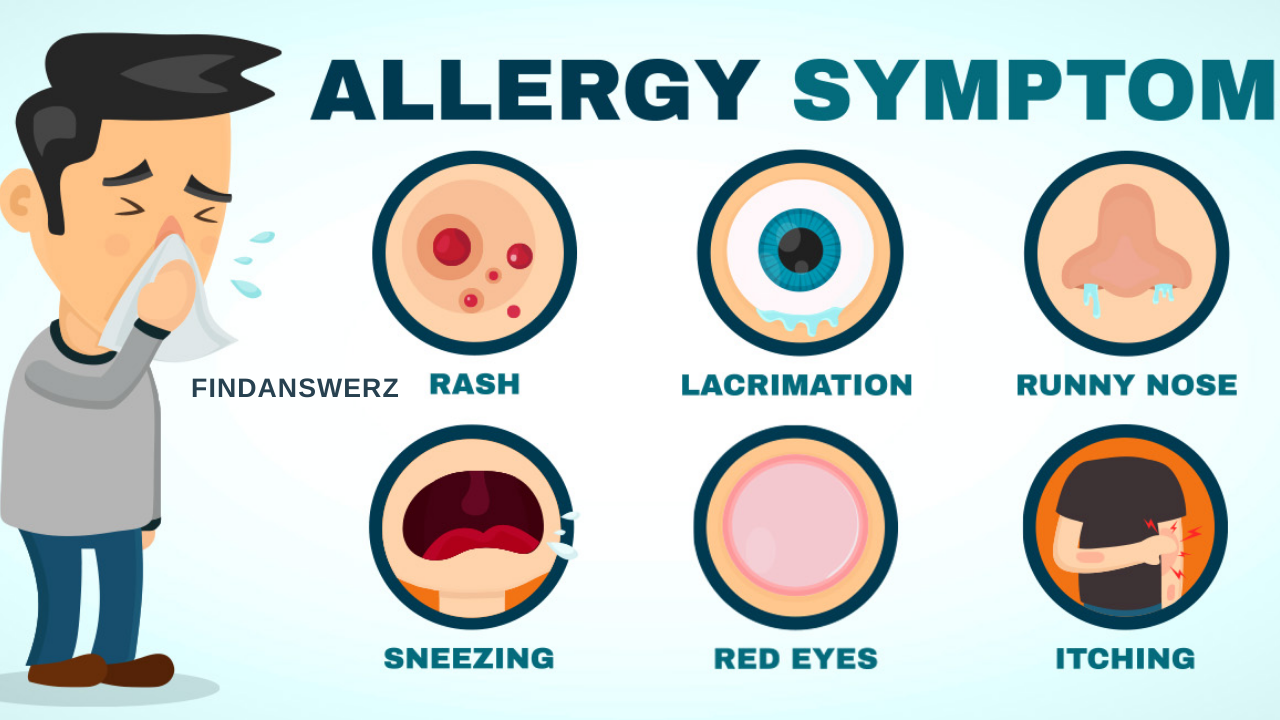
Understanding Allergies in Kids
Allergies occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless substance, such as pollen or food, as harmful. The body then produces an immune response to fight off what it perceives as a threat. Children can develop allergies at any stage of life, but many allergies start in early childhood. These allergic reactions can range from mild symptoms to life-threatening conditions such as anaphylaxis, making it important for parents to be vigilant.
Common Types of Allergies in Kids
There are several common allergens that can affect children. These allergens can trigger a range of reactions, from sneezing and hives to more serious conditions. Understanding these allergies is the first step in managing them.
1. Food Allergies
Food allergies are among the most common allergies in children. Common food allergens include:
- Peanuts and Tree Nuts: These allergies can be severe, with reactions ranging from hives to anaphylaxis.
- Dairy: Milk protein allergy is particularly common in young children and can cause skin reactions, digestive issues, and even respiratory problems.
- Eggs: Some children are allergic to the proteins found in eggs, which can cause symptoms like skin rashes or digestive discomfort.
- Wheat: Wheat allergies are often confused with gluten intolerance but involve a different immune response.
- Shellfish and Fish: These allergies are typically lifelong and can lead to severe reactions in some children.
The Benefits of Regular Detoxes: Unlocking Your Body’s Full Potential
Symptoms of food allergies include:
- Hives or rashes
- Swelling of the lips, face, or throat
- Vomiting or diarrhoea
- Difficulty breathing
- Anaphylaxis (severe, life-threatening allergic reaction)
2. Environmental Allergies (Hay Fever)
Environmental allergens are substances found in the air that can trigger allergic reactions. These include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Seasonal allergies, often called hay fever, are common in the spring and fall when pollen levels are high.
Symptoms of environmental allergies include:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Itchy eyes, nose, or throat
- Coughing and wheezing
- Asthma exacerbation
3. Insect Sting Allergies
Insects such as bees, wasps, and hornets can trigger allergic reactions in some children. An allergic reaction to an insect sting can be mild, causing localized swelling and pain, or more severe, leading to systemic reactions such as anaphylaxis.
Symptoms of insect sting allergies include:
- Swelling at the sting site
- Itching and redness
- Nausea, vomiting, or dizziness
- Difficulty breathing (in severe cases)
4. Drug Allergies
Although less common, children can also develop allergies to medications. These reactions can occur with antibiotics, such as penicillin, or other medications. Drug allergies can cause symptoms ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylactic reactions.
Symptoms of drug allergies include:
- Skin rashes or hives
- Swelling of the face or limbs
- Fever or flu-like symptoms
- Difficulty breathing
5. Skin Allergies (Contact Dermatitis)
Skin allergies can be caused by contact with certain substances such as soaps, lotions, or fabrics. A condition known as eczema or atopic dermatitis is common in children and can make the skin more sensitive and prone to irritation. Contact with allergens like poison ivy or certain fabrics can lead to allergic reactions.
How to Recover Quickly From Common Illnesses: Tips for a Speedy Recovery
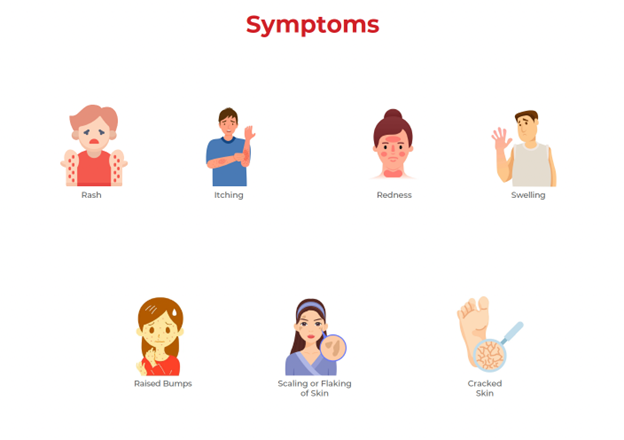
Symptoms of skin allergies include:
- Itchy, red, or inflamed skin
- Blisters or bumps on the skin
- Dry, flaky patches of skin
Recognizing Symptoms of Allergies in Kids
Identifying the signs of an allergic reaction in children is crucial for timely treatment. The symptoms can vary widely depending on the type of allergy, and they may range from mild to severe. Early detection and proper management are essential in preventing complications.
1. Mild to Moderate Symptoms
- Sneezing or coughing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Watery, itchy eyes
- Skin rash or hives
- Swelling in the face or lips
2. Severe Symptoms (Anaphylaxis)
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Swelling of the throat or tongue
- Dizziness or fainting
- A rapid or weak pulse
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Loss of consciousness
If your child exhibits symptoms of anaphylaxis, it is crucial to administer epinephrine (if prescribed) immediately and call 911.
Managing Allergies in Kids
Once you have identified the type of allergy, the next step is to develop a strategy to manage it. Managing allergies in children requires a combination of avoiding allergens, using medications, and knowing when to seek medical attention.
1. Avoiding Allergens
The best way to prevent allergic reactions is to avoid the substances that trigger them. Here are some strategies for common allergens:
- Food Allergies: Educate your child about their food triggers, and always read ingredient labels. In restaurants, make sure to inform the staff about your child’s food allergies.
- Environmental Allergies: Keep windows closed during high pollen seasons, use air purifiers, and encourage your child to wash their hands and face after playing outside. Use dust mite-proof bedding and vacuum frequently.
- Insect Allergies: Avoid areas where insects are likely to sting, such as flowers or tall grass. Keep your child dressed in protective clothing when outdoors. Always carry an epinephrine injector if your child has a known insect sting allergy.
- Drug Allergies: Always inform your healthcare provider about your child’s known drug allergies. Carry a list of medications to avoid.
2. Medications
There are several medications that can help manage symptoms of allergies in children:
- Antihistamines: These over-the-counter medications can help relieve symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. They can be taken in liquid, chewable, or pill form.
- Decongestants: These can help relieve nasal congestion, but they should only be used for short periods, as they can have side effects.
- Steroid Nasal Sprays: These can be prescribed for more severe nasal allergies and are effective in reducing inflammation in the nasal passages.
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline): For children with severe allergies, especially food or insect sting allergies, a prescription for an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) may be necessary. This can stop anaphylaxis and buy time until emergency medical help arrives.
3. Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots)
For children with persistent allergies, allergists may recommend immunotherapy, which involves a series of allergy shots to help the child gradually build up immunity to specific allergens. This treatment is especially useful for environmental allergies.
4. Emergency Plans and Action Steps
If your child has a known allergy, it is essential to have an emergency plan in place. The plan should include:
- Identification: Clearly identify allergens that affect your child and provide information about them to school personnel, caregivers, and anyone else who interacts with your child.
- Medication: Make sure your child always has access to the necessary medication, including antihistamines, epinephrine auto-injectors, and other prescribed treatments.
- Communication: Ensure that your child’s school, caregivers, and family members are well-versed in your child’s allergy management plan.
Prevention Tips for Allergies in Kids
While you cannot entirely prevent allergies, there are several steps you can take to reduce the risk of developing them:
- Breastfeeding: Studies suggest that breastfeeding can help strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of allergies in babies.
- Avoidance of Smoking and Pollutants: Exposure to cigarette smoke and other environmental pollutants can increase the risk of developing allergies, so it’s important to maintain a clean, healthy environment.
- Introduce Allergenic Foods Early: Some research suggests that introducing potentially allergenic foods such as peanuts and eggs early in a child’s life may help reduce the risk of developing food allergies.
When to See a Doctor
If you suspect your child has an allergy, it’s crucial to consult with a pediatrician or an allergist. A healthcare provider can help identify the cause of your child’s symptoms and recommend the most effective treatments. In severe cases, allergy testing may be necessary to pinpoint specific allergens.
If your child experiences a severe allergic reaction, seek emergency medical help immediately.
Handling allergies in kids can be challenging, but with the right approach, it is possible to manage the symptoms and minimize the risks. By understanding common allergies, recognizing symptoms, and taking proactive steps to avoid allergens, you can significantly improve your child’s quality of life. Always stay vigilant, communicate with caregivers and teachers, and consult with healthcare providers to ensure your child is well-prepared to handle any allergic reactions that may occur.

